What is Ultraviolet radiation?
July is UV Safety Awareness Month
As we bask in the warmth and light of the sun, it's essential to understand the invisible companion that accompanies it: Ultraviolet (UV) radiation. This form of energy, while playing a critical role in various natural processes, doesn't come without its risks. While we often relish the sun's warmth and the golden tan it can provide, it's crucial to be mindful of the fine line between healthy exposure and the potential dangers that overexposure can bring, such as skin damage, premature aging, and increased risk of skin cancer. Keep reading to learn more about UV radiation, its impacts, and how we can enjoy the sun safely, protecting ourselves and our loved ones from its less favorable effects.
#1 type of cancer in America is skin cancer.
5 or more sunburns double your risk for melanoma, the deadliest form of skin cancer.
20% of cataract cases may be caused by overexposure to UV radiation.
Types of UV Radiation
There are 3 main types of UV radiation, each affecting humans in differing ways. The types of UV radiation are classified based on their wavelengths.
Wavelength
UV Light has a shorter wavelength than visible light, and each type of UV light has a different length therein.
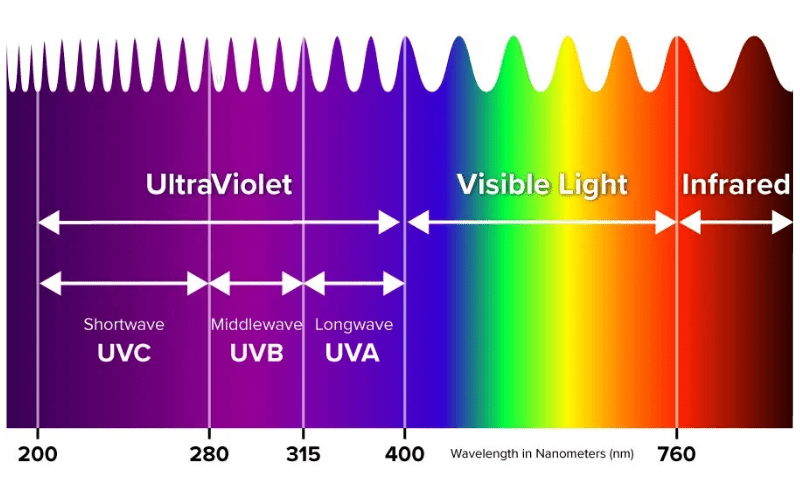
UVA
UVA rays make up the majority of UV radiation reaching the Earth’s surface and are primarily responsible for skin aging and wrinkling and have also been associated with skin cancer. They can cause damage to the skin cells called keratinocytes in the basal layer of the epidermis, where most skin cancers occur. UVA exposure can lead to indirect DNA damage by generating free radicals that can harm cells.
UVB
UVB rays are less prevalent than UVA rays but are more intense. They are primarily responsible for direct damage to the skin’s DNA and are the main cause of sunburn. They can also contribute to premature skin aging but to a lesser extent than UVA rays.
UVB radiation plays a critical role in the body’s natural production of vitamin D.
UVC
UVC rays have the shortest wavelength and are the most harmful type of UV radiation. However, they are completely absorbed by the Earth’s atmosphere, particularly the ozone layer, and do not reach the Earth’s surface. Due to their absorption by the atmosphere, natural UVC rays do not pose a risk to human skin or eyes.
Effects of UV Radiation
As previously mentioned, UV radiation can cause damage to human skin and eyes. Here, we will explore the impact of UV exposure further.
Sunburn
Sunburn is a painful inflammation of the skin triggered by overexposure to UV radiation from the sun, tanning beds, or sun lamps. The severity of sunburn can vary widely; mild cases might result in slight tenderness, while more severe instances can cause intense pain, blistering, or even fevers—conditions that warrant immediate medical attention.
Skin Aging & Cancer
Exposure to UVA and UVB rays without adequate protection can harm skin cells’ DNA, leading to genetic mutations that may result in skin cancer and accelerated aging. Additionally, these UV rays pose a risk to eye health, potentially causing conditions such as cataracts and cancers of the eyelids.
Immune Suppression
UV radiation can harm the communication between cells, making it difficult for them to build defenses against bacterium and viruses. Additionally, it may cause our body to release signals that tell the immune system to weaken its defenses when it should actually be alert.
Eye Damage
Extended exposure to UV rays can alter the proteins in the lens of the eye, resulting in the development of cataracts which can progressively impair vision, making it blurry, dull, or less vibrant. Additionally, prolonged UV exposure is associated with an increased risk of eyelid cancers, such as basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma.
Staying Safe in the Sun
Thankfully, there are many ways you can protect yourself from the effects of UV radiation while enjoying outdoor activities! Remember, UV radiation is not only present on sunny days, so make sure you protect yourself year-round.
Wear Sunscreen
Sunscreen acts as a barrier that either absorbs or reflects the sun’s UV rays, preventing them from penetrating the skin. SPF stands for Sun Protection Factor, a measure of how well a sunscreen can protect the skin from UVB rays. The SPF number indicates how much longer you can stay in the sun without getting sunburned compared to if you weren’t wearing any sunscreen. For example, an SPF of 30 means you could theoretically stay in the sun 30 times longer without getting burned. It’s important to choose a “broad-spectrum” sunscreen, which protects against both UVA and UVB. Dermatologists generally recommend using a sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30, which blocks about 97% of UVB rays. If you’re swimming or sweating, look for water-resistant sunscreen, but remember to reapply every two hours or immediately after swimming or sweating heavily.
Pro Tip: Wear sunscreen every day, not just when you are going outdoors!

Wear Sunglasses
Sunglasses protect your eyes from harmful UV rays and reduce glare from reflective surfaces, making activities like driving or being on the water safer and more comfortable. Ensure your sunglasses offer 100% protection against both UVA and UVB rays. The level of UV protection is not dependent on the darkness or color of the lenses. Wraparound sunglasses offer better protection by blocking UV rays that might enter from the sides. Children’s eyes are more susceptible to UV damage because they have larger pupils and clearer lenses, allowing more light to penetrate. UV rays can penetrate clouds, so wearing sunglasses on overcast days is still important. For those who wear prescription glasses, consider photochromic lenses or prescription sunglasses to ensure clear vision while protecting your eyes from UV rays.

Wear Protective Clothing
Protective clothing provides a physical barrier between your skin and the sun’s rays. Unlike sunscreen, which can wear off or be applied too thinly, clothing offers consistent protection as long as it covers the skin. Tightly woven or knitted fabrics provide better protection than loosely woven ones. Darker or brighter colors tend to absorb more UV rays than lighter colors, reducing the amount of radiation that reaches your skin. Many outdoor clothing brands now offer garments specifically designed with UV-protective fabrics. Opt for long-sleeved shirts and long pants or skirts to cover as much skin as possible. The more skin you cover, the better your protection. A wide-brimmed hat can provide shade and protection for your face, ears, and neck—areas particularly vulnerable to sun damage. The effectiveness of protective clothing can diminish over time, especially with repeated washing and wear. Regularly update your protective wardrobe to maintain optimal UV defense. Some laundry detergents now include UV-blocking agents that can enhance the protective power of your clothes after washing.
Avoid Tanning
As highlighted earlier, tanning is an indicator of skin harm. Exposure to UV rays, whether from the sun or artificial sources, greatly heightens the chances of skin cancer and accelerates aging. Despite this knowledge, some people monitor the UV index to sunbathe when it’s high, not realizing that a higher UV index means greater risk of skin damage. For those yearning for a bronzed look, safer options exist, such as self-tanning lotions, sprays, and wipes, which offer a sun-kissed glow without the dangers of UV radiation. Remember, these alternatives do not provide sun protection, so applying sunscreen remains essential. Additionally, maintaining well-hydrated skin can enhance its natural beauty and health, reducing the allure of tanning for cosmetic purposes.
resources
Educational Resource
American Academy of Dermatology Association
With a membership of more than 20,500 physicians worldwide, the AAD is committed to: advancing the diagnosis and medical, surgical, and cosmetic treatment of the skin, hair, and nails; advocating high standards in clinical practice, education, and research in dermatology; and supporting and enhancing patient care for a lifetime of healthier skin, hair, and nails.

Any Florida BLue Member 18+
Next Steps Health Coaching
Experience individualized health coaching with the Florida Blue Next Steps Health Coaching program. Health coaching is free for all Florida Blue members who are ages 18+ and is available through phone and email with a Registered Nurse Certified Health Coach.
During these one-on-one sessions, discuss health and wellness topics that matter to you.

Get the help you need
Find a Provider
Scheduling regular health check-ups is crucial, even if you feel perfectly healthy. These check-ups can play a pivotal role in early detection of conditions like skin cancer, which is especially important since early diagnosis significantly improves treatment outcomes. Dermatologists can conduct thorough skin examinations to spot any unusual changes or abnormalities that might be overlooked otherwise.

More Blog Posts
Safe Toys and Gifts Awareness
why is toy safety Important?December is Safe Toys and Gifts Awareness MonthDecember is the biggest gift-giving month in the world. Holiday shopping…

Celebrating our Wellness Team: Gold Well…
We are thrilled to announce that the GatorCare wellness team has been honored with the prestigious Gold Well Workplace Award from the Wellness…

December 2024 Better You Newsletter
Stay healthy this holiday season with our Better You Newsletter!
